why is constant head permeability test important|constant head permeability test pdf : Brand manufacturer 1. Constant Head Permeability Test. 2. Variable Head or Falling Head Permeability Test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval. Constant head method is suitable for . webAcompanhantes e garotas de programa em Mandaguari (Paraná). Contato com as garotas mais sensuais e liberais de Mandaguari (Paraná). Acompanhar mulheres em .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sonhar com rato significa presságios negativos. É o símbolo .
The constant head test method is used for cohesionless and more permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for cohesive or less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s). The constant head permeability method is espoused in this manual for determining the permeability of sandy soil. See more
Constant Head Permeameters measure the coefficient of permeability of non-plastic soils with no more than 10% of particles passing a 75µm (No. 200) test sieve. The procedure described in AASHTO T 215 is also a withdrawn .1. Constant Head Permeability Test. 2. Variable Head or Falling Head Permeability Test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval. Constant head method is suitable for .The objective of constant head permeability test is to determine the coefficient of permeability of a soil. Coefficient of permeability helps in solving issues related to: Yield of water bearing strata. Stability of earthen dams. Embankments of .
The Constant Head Permeability Test, also known as the constant head test, analyzes coarse-grained soils like sands and gravels. It maintains a constant hydraulic .
The purpose of this test is to determine the permeability (hydraulic conductivity) of a sandy soil by the constant head test method. There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely . Constant Head Test In this test the differential pressure (the head) across the sample remains constant throughout the test. This test is equally valid for gravel, sands and clay soils.Falling Head Permeability Test. Why is this test done? This test is used to determine the coefficient of permeablity of a soil. This is important in examining the movement of contaminants through soil or when characterizing flow nets. .
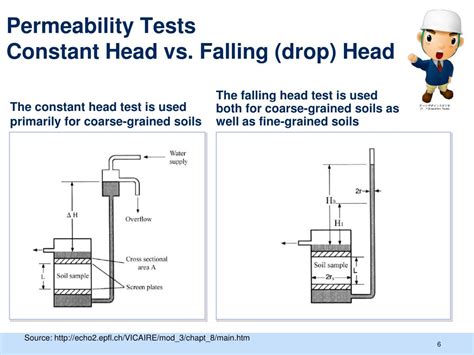
This document examines the concept behind permeability (Darcy’s Law), why the coefficient of permeability is important, and explains the Constant Head Permeability Testing Method, which is the Test method .Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test .
In a constant head permeability test (Fig. 7.6), the total head loss (hL) across a cylindrical soil specimen of length L and cross sectional area A, is maintained constant throughout the test, and at steady state, the flow rate (Q) is measured. L A L hL measuring cylinder Figure 7.6 Constant head permeability test
Permeability Test Method 1 for consolidated material is used only within the vadose zone and is the preferred method if the packer test method cannot be used. The principal problem of any gravity permeability test method is that a uniform supply of water is necessary so that a constant head can be maintained above the static water surface.Permeability is a property of porous materials that is an indication of the ability for fluids (gas or liquid) to flow through them. Fluids can more easily flow through a material with high permeability than one with low permeability. [1] The permeability of a medium is related to the porosity, but also to the shapes of the pores in the medium and their level of connectedness. [2]The permeability is a measure of the ease with which liquids and gases can pass through a rock. The more consolidated the material, the lower its permeability. Thus "loose" materials like gravel have high permeability. Some rocks can also have anisotropic permeability, meaning that fluids can flow easily in one direction, but not in another. And in environmental management, assessing soil permeability is very important in controlling erosion, managing runoff, and protecting water quality. . The constant head permeameter test measures the flow of water through soil that is well-drained, like sandy or gravelly soils. I found this method straightforward in areas of my garden where .
Trenchlesspedia Explains Permeability Test. There are two methods to perform the soil permeability test – the constant head method and the falling head method. In the constant head test, the same relative elevation of the top of the water column remains over the sample for the entire duration of the test.
constant head test vs falling
The Constant head permeability test follows the principle of Darcy’s Law [29] and therefore, it is . The same number of samples than the one regarded as the falling head permeability test was considered. It is important to notice that the assembly of the constant head permeability test is easier and faster than the one of the falling head .
Darcy’introduced a constant of proportionality called the Darcy Coefficient of Permeability, k and Eq. 2 becomes: Commonly in civil engineering k is called simply hydraulic conductivity or the coefficient of permeability or, even more simply, the Permeability. Eq. 3 is called Darcy’s law. It was primarily based on the It's because of the practical aspect of the test and measuring the water, not for the fact of it being constant or falling. For clay, the falling test is more common, because water volume gets measured very easily as the head in the .There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s).
ASTM D 1653 is a standard test method used to determine the permeability of organic coatings to water vapor and gases. . The permeability of coatings is an important property to measure, as it can impact the overall performance and durability of the coating. Coatings that are permeable to water or other substances can allow them to penetrate .
Laboratory consolidation test results for a sample of the clay at a depth of 15 feet below the ground surface reveal a preconsolidation stress of 2,400 psf, compression index of 0.5, recompression index of 0.1 and initial void ratio of 0.66. Now a falling or constant head permeability test may be conducted, depending on the type of soil. The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 .D 4254 Test Methods for Minimum Index Density of Soils and Calculation of Relative Density3 3. Fundamental Test Conditions 3.1 The following ideal test conditions are prerequisites for the laminar flow of water through granular soils under constant-head conditions: 3.1.1 Continuity of flow with no soil volume change during a test,PART I. CONSTANT-HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily to. determine the suitability of sands .
Permeability influences the rate of settlement of a saturated soil under load. The stability of slopes and retaining structures can be greatly affected by the permeability involved. The design of earth dams is very much based .In a constant-head permeability test, the length of the specimen is 200 mm and the cross-sectional area is 78.5 cm^2. If k = 2.1 times 10^-2 cm/sec, and a rate of flow of 130 cm^3/min has to be maintained during the test, what should be the head difference across the specimen?Permeability k is calculated for constant head tests using. where. q is the constant rate of flow. H c is the constant excess head (measured relative to original groundwater level) F is the shape factor (from Figure 12.10) As with the other equations in this chapter, care must be taken to use consistent units.
Here is a comparison of the constant head and falling head permeability. The constant head test is used to determine the coefficient of permeability (k) of soil by applying a constant water charge to sample, measuring the quantity of water flowing through the specimen over time. . Conversely, the falling head permeability test allows the . Permeability Definition - Why is it Important in Civil Engineering? Permeability Definition: Permeability of soil is a measure of the . Falling Head and Constant Head Method Permeability Test. Arjun Barman,CE Meet Arjun Barman, a civil engineering enthusiast on a mission to become a structural engineering maestro. With an unwavering passion . 1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of permeability of granular soils that may occur in natural deposits as placed in embankments, or when used as base courses under pavements.Soil permeability is the property of the soil to transmit water and air and is one of the most important qualities to consider for fish culture. . a column of soil is placed under specific conditions such as water saturation and constant head of water . Repeat the permeability test until you measure a nearly constant value for seepage; .
The constant head permeability test involves flow of water through a column of cylindrical soil sample under the constant pressure difference. The test is carried out in the permeability cell, or permeameter, which can vary in size depending on the grain size of the tested material. The soil sample has a cylindrical form with its diameter being . The schematic diagram for the constant head method is shown in Fig. 5(a), and Fig. 5(b) shows the experimental test setup assembled at the laboratory. For testing the slabs by the constant head method, a square wooden tank of size 1.2 m × 1.2 m × 0.4 m was assembled, as shown in Fig. 5(b). The inner side of the wooden tank was covered with a .tion of coefficient of permeability of soils using falling head and the constant head methods. This test is recommended for soils with coefficient of permeability in the range lo- 3 to 10-v cm/s and maximum particle size of 9.5 mm. 2. TERMINOLOGY 2.1 For the purpose of this standard, definition terms given inSynopsis The theory of the in situ constant head permeability test (Gibson, 1963) is shown to be strictly valid only if the soil behaves as a porous perfectly elastic medium. For this ideal soil the flow rate is given by an expression which holds not only for inflow and outflow tests, but also for either a rigid or an infinitely compressible piezometer tip, i.e. a spherical cavity. The theory .
In a laboratory, a constant head permeability test was conducted on a brown sand with a trace of mica. For the constant head permeameter, the following data were obtained: Quantity of water discharged during the test = 250 cm Length of specimen between manometer outlets = 11.43 cm Time required for given quantity of water to be discharged = 65 sec. Head difference .
constant head test pdf
Resultado da Con gratismediumchat.nl/es puedes chatear en línea, 100% libre de cargo con médiums, videntes, psíquicos, lectores de tarot, sanadores y otros ayudantes espirituales. Actualmente ya no es raro contactar a un médium o un adivino.
why is constant head permeability test important|constant head permeability test pdf